3D NAND Flash uses vertical architecture to provide high performance. Explore how it works, the types of NAND and its pros & cons. Click here now.


3-D NAND is the most advanced form of NAND, enabling greater speed, lower cast and higher density than earlier versions of NAND.
First, let’s take a quick glance back. NAND is non-volatile flash memory storage that does not need power to retain data. NAND storage appears in a wide range of products, from small consumer devices to high-capacity SSDs in flash-based enterprise data centers.
However, 2D NAND – also called planar NAND – has reached the limits of its capacity development. 2D NAND capacity growth is constrained by how many memory cells can fit within finite width and length dimensions.
Although manufacturers attempted to grow NAND capacity by shrinking cell sizes, the experiments did not deliver. Problems occurred due to cell sizes and electrons. 2D NAND cells must have enough space to store sufficient electrons. If there are too few electrons because the cell is too small, then cell functioning decreases and cell-to-cell interference increases. Performance, endurance, and reliability all suffer.
This is where 3-D NAND comes in.
3D NAND, also called Samsung V-NAND, was developed to overcome 2D NAND’s capacity limitations. 3D NAND architecture scales to higher densities without sacrificing data integrity.
Unlike planar NAND where memory cells are stacked horizontally on cards, 3D NAND is stacked vertically using multiple layers to achieve higher density, lower power consumption, better endurance, and faster reads/writes, and a lower cost per gigabyte. Because it packs so many vertical cells into small width and length dimensions, 3D NAND has far more capacity than 2D NAND within the same length and width dimensions.
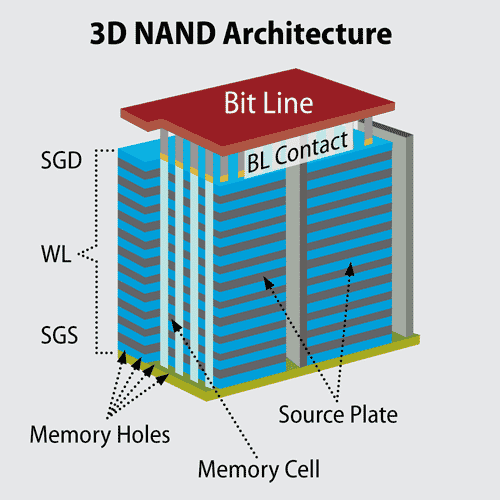
3D NAND uses advanced architecture to provide high performance in a flash environment.
NAND comes in different bit counts per cell, which impacts performance and durability. NAND cells contain 1,2, 3, or 4 bits: SLC, MLC, TLC, and QLC. 3D NAND also comes in MLC, TLC, and QLC, but not SLC. For more background, you may want to compare SLC vs. MLC vs. TLC.
Research and Markets “Global NAND Flash Market 2018-2020” report projects the global NAND market to grow at a CAG of 15.13% from 2018 to 2022. The projection includes both planar and 3D NAND, and states that 3D NAND adoption is a key growth driver in the market growth.
However, there are pricing pressures on 3D NAND.
Given these challenges, is 3D NAND still better than planar NAND?
The broad answer is yes. 3D NAND is a proven, cost-effective technology that is in the market now. It offers better energy efficiency, higher performance read/write and I/O, and much higher capacity than 2D NAND at lower cost per GB.
Adopting 3D NAND takes some investment in retooling storage infrastructure and transitioning storage. But this temporary pain is worth the benefits for high data growth/high performance environments.


Christine Taylor is a writer and content strategist. She brings technology concepts to vivid life in white papers, ebooks, case studies, blogs, and articles, and is particularly passionate about the explosive potential of B2B storytelling. She also consults with small marketing teams on how to do excellent content strategy and creation with limited resources.

Enterprise Storage Forum offers practical information on data storage and protection from several different perspectives: hardware, software, on-premises services and cloud services. It also includes storage security and deep looks into various storage technologies, including object storage and modern parallel file systems. ESF is an ideal website for enterprise storage admins, CTOs and storage architects to reference in order to stay informed about the latest products, services and trends in the storage industry.
Property of TechnologyAdvice. © 2026 TechnologyAdvice. All Rights Reserved
Advertiser Disclosure: Some of the products that appear on this site are from companies from which TechnologyAdvice receives compensation. This compensation may impact how and where products appear on this site including, for example, the order in which they appear. TechnologyAdvice does not include all companies or all types of products available in the marketplace.